Birthmarks and Everything You Need to Know About Them
If you have any birthmarks anywhere in your body, you are among more people than you think. Apparently, over 80% of babies are born with some kind of a birthmark. While some disappear in childhood, others may last for a lifetime, well, if you do nothing about them.
So, what are birthmarks, and how do they form? Are there different types and can one get rid of birthmarks? These are some of the questions that may run through your mind every time the mark stares back at you.
To answer these and any other questions that you may have, we will take you through birthmarks and everything you need to know about them. Indulge yourself below:
What are Birthmarks?
Birthmarks are a type of skin discolourations or alterations in texture that are usually visible at birth or soon after. They can also appear as raised irregularities which are generally benign. They come in various sizes ranging from pin-sized spots to large marks.
They can occur in different parts of the skin, anywhere from the face to the sole of the foot. Also, they vary in colour and appearance depending on your skin colour. Common colours include black, brown, red, purple and pink.
Birthmarks can be permanent or temporary, while others can grow larger with time. They can also vary in texture ranging from smooth to hairy while others tend to be warty or sitting on a stem.
What Causes Birthmarks?
While Science has not yet provided a definitive answer to what causes birthmarks, they can be linked to two scenarios; accumulation of melanocytes (the melanin-producing cells), or overgrown/dilated blood vessels. It is from this basis that the two main categories of birthmarks are formed. These are vascular birthmarks and pigmented birthmarks.
Where Science falls short, myths take over; some folklore has it that these blemishes are caused by unsatisfied cravings during pregnancy. Birthmarks have also been used to foretell futures; for example, birthmarks occurring on the chin are associated with success.
Have you also been told that your birthmark is a result of your mother’s emotions when she was expectant? These are just but a few of the many myths which have nothing to do with the formation of birthmarks.
Can Birthmarks be Genetic?
Some birthmarks also appear to be hereditary, in that some family members have similar marks. In such cases, these spots occur on the same part of the body. Such spots are caused by genetic mutations.
These are rare and caused by conditions such as Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome (failure of blood or lymph nodes to form correctly) and Sturge-Weber syndrome (neurological skin disorder).
Types of Birthmarks
As mentioned above, birthmarks are classified into two categories which are further broken down into different subtypes. The distinction is made depending on the appearance of the marks and how they are formed.
Vascular Birthmarks
These are as a result of either malformation of blood vessels or their accumulation into one area which makes them visible through the skin. Vascular birthmarks include:
a) Infantile haemangioma
These are commonly referred to as ‘strawberry’ birthmarks. They are mostly formed on the face, head or neck. They appear blue, purple or bright red in colour though they start as white or pink and progress. The haemangiomas can be superficial, deeper into the skin or a combination of both.
They are usually found in newborns but may also appear within the first few weeks of a baby’s life. If you are reading this, you are less likely to have them as they typically disappear by 10 years of age.
b) Salmon patches (Nevus simplex)
These are salmon coloured, pink or red birthmarks. They are among the most common birthmarks; prevalent among 80% of newborns. Salmon patches usually occur on or near the face.
On the neck, they are referred to as “stork bites/marks” and “angel kisses” when they occur on the forehead, face and eyelids.
Most of these marks are harmless, temporary and fade away by the time your baby is two years old. Don’t be surprised if they reappear when your baby cries!
c) Capillary malformation
These are red or purple marks that commonly occur on the face, but can also form on the arms and legs. They originate from abnormal growth of blood vessels in the skin, hence the name capillary malformation. Commonly, they are known as “port wine” stains.
Typically, these birthmarks are harmless, but most parents prefer to opt for treatment. Reason being, these marks don’t fade with age and removal is sometimes necessary albeit for cosmetic reason. Paediatric dermatologists usually recommend treatment using pulsed dye laser during the first few months after birth.
Pigmented Birthmarks
These are birthmarks formed due to extra pigmentation on the skin. They range in colour from light brown marks to dark blue ones. Here are the main types of pigmented birthmarks:
a) Moles (Congenital nevi)
Moles can be raised or flat and come in different colours such as pink, brown or black. Typically, they are round-shaped and can occur anywhere on the body. These raised birthmarks can disappear with time, but some stick around forever.
Moles can be worrisome, especially if they are large (more than 1 inch / 2.5cm), have little hairs and change colour with time. These are more likely to become cancerous hence need periodical observation by a qualified dermatologist.
b) Café au lait spots
These are light brown coloured birthmarks aptly named after a French phrase meaning “coffee with milk”. They are permanent and occur in about 20% of newborns.
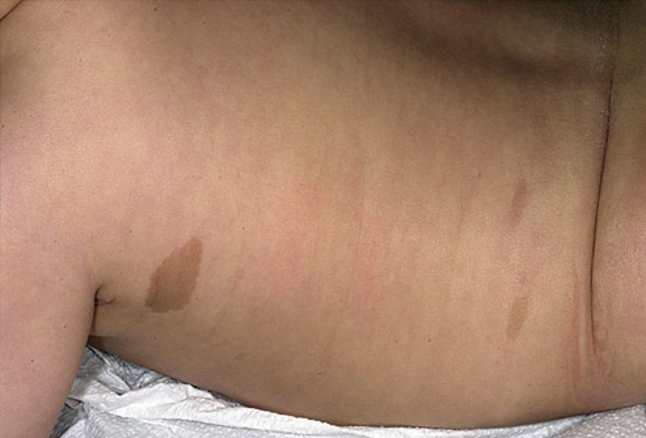
Also known as Café au lait macules, these marks are mostly benign and usually not a cause for worry. However, if they are five or more, it’s advisable to consult a paediatrician; to rule out genetic conditions that result in skin cancer.
c) Mongolian spots (Dermal melanocytosis)
These are dark blue marks that can sometimes appear like bruises. These birthmarks are mostly unique to people with dark skin colour. They can occur anywhere on the body but are usually found around the lower back and buttocks.
At a young age, they can be a source of worry since they are quite large. You should, however, take solace in the fact that they are benign, fade with time, and typically disappear by the age four.
Can Birthmarks Appear Later in Life?
Birthmark-like spots can appear later in life. Such spots are, however, not considered birthmarks. The distinction is that a spot or mole can only be a birthmark if it appears at birth or shortly after that.
Complications with Birthmarks
Should I be worried about my baby’s birthmarks? This is a common question, especially from first-time mothers. While most of these marks are harmless and fade away with time, some can be indicators of underlying medical conditions. Also, as earlier noted, others can be cancerous tumours.
Here is what to be on the lookout for;
● Changes in colour and size
● Multiplication of moles
● Unusually large mark
● Bleeding, itching and formation of sores
● Development of irregular edges
If a birthmark(s) shows any of the above, consult a dermatologist immediately.
How to Get Rid of Birthmarks
Birthmarks can be a source of pride for some people and as such, are seen as beauty spots. In fact, unless any of the above signs causes concern, you and your birthmark can coexist harmoniously.
On the other hand, let’s face it; birthmarks can make you self-conscious, especially since they don’t follow set rules as far as size, colour, shape and location are concerned. Luckily, you don’t have to live with one just because it is harmless; both vascular and pigmented birthmarks can now be successfully removed or faded.
There are several options for birthmark removal at your disposal:
#1 Laser Therapy
Laser therapy involves the use of concentrated beams of light to treat the skin. Laser birthmark removal is targeted at both the vascular and pigmented birthmarks.
For vascular birthmarks, the laser is targeted at the haemoglobin in the blood, which is concentrated in the birthmarks. The idea is to vaporise the blood, which leads to the destruction of the micro-vessels.
Once they collapse, the body gets rid of the destroyed bits to reveal birthmark free skin. Darkening of the birthmark is a sign that the healing process is underway. You may require up to 8 treatments in intervals of 1-3 months, depending on how complex or deep the birthmark is.
As for the pigmented type, the laser seeks to alter the molecular structure of melanin. When this happens, the body’s immune system can easily break it down and eliminate it. As with the vascular birthmark removal, several sessions are also required depending on the severity of your condition.
Sometimes, melanin inhibiting creams are used in combination with the treatments to prevent post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
#2 Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers are common with ‘strawberry birthmark’ removal. So what’s the process? In your heart, there are receptors called beta-adrenergic receptors. When stimulated, they increase your heart rate, leading to pumping of more blood throughout your body. The haemangiomas, therefore, look full and ‘colourful’.
Beta-blockers like propranolol inhibit the beta-adrenergic receptors hence reducing the blood supply. This shrinks them, makes them look softer and reduces their colour. Propranolol is also known to inhibit the growth of haemangioma cells, which gradually diminishes their size until they are no more.
#3 Corticosteroids
Some types of birthmarks, such as large haemangiomas can be shrunk by use of steroid-based medication. Corticosteroids are used in these treatments and can be administered orally, topically or through injection. They are usually recommended for people who do not respond well to beta-blockers.
These are anti-inflammatory medications that work in the blood vessels directly. Corticosteroids are effective and rapidly reduce the size of birthmarks within a few weeks.
Steroids are however associated with a host of side effects. Such include low blood pressure, depression, insomnia and adrenal gland insufficiency. For this reason, the medication should only be prescribed in low dosages and by qualified doctors.
An alternative to corticosteroids is the drug Interferon alfa-12. It works by stopping blood flow to the raised birthmark and stimulating white blood cells to kill haemangioma cells.
#4 Surgery
When none of the above works, you might want to try cosmetic surgery. Surgical removal or excision is recommended for severe birthmarks that can cause complications such as port-wine stains and haemangiomas.
With significant enlargement, these marks can encompass large areas and in some cases affect eyesight and hearing. In such cases, surgery becomes the only way to restore symmetry and remove unwanted tissue.
Depending on the severity, a skin graft might be necessary to cover the affected area. Surgery will usually call for at most 5 days of hospital stay and about 6 weeks for a full recovery.
There can, however, arise complications such as ulcerated sores and bleeding; this calls for expert medical diagnosis and review, before and after treatment.
Can Birthmarks be Removed without Surgery?
Yes, advances in surgical procedures have seen the rise of minimally invasive birthmark treatments such as cryosurgery and electrodessication:
● Cryosurgery/Cryotherapy
This is the use of extreme cold to destroy abnormal tissue. The pigmented cells are frozen and die, and are slowly absorbed by the body.
This outpatient procedure uses a cotton swab dipped in a refrigerant such as liquid nitrogen. A spray bottle may also be used. To minimise pain and discomfort, numbing medicine is usually administered before treatment.
Side effects associated with the procedure include; blisters, damage to nearby tissue, scarring and ulcers.
● Electrodessication and Curettage (ED&C)
This is a birthmark removal method which desiccates tissue by dehydration, followed by scraping off (curettage). The affected area is first numbed off before the electric current is delivered to superheat the skin.
Typically the numbing agent used in this procedure is lidocaine, which is injected into the skin. Once the process is done, the wound is bandaged and remains covered for about 2 days. Pain relief medication may be prescribed as part of post-treatment care.
The procedure is highly effective and is not associated with many side effects. However, regular exams may be recommended to ensure that the scar heals well.
Using Birthmark Removal Creams
The cosmetic and beauty industry has seen strides in the development of products that reduce the appearance and get rid of skin blemishes. Such include birthmark fade creams that act on pigmented birthmarks. Active ingredients in the formulations work by inhibiting melanin production in the treatment area.
With melanin suppression, cells and tissue lose their characteristic dark or brown pigmentation. For example, hydroquinone, one of the most potent and most common skin lighteners, destroys pigmented cells and inhibits tyrosinase, the enzyme involved in melanin synthesis.
While skin lighteners can be effective, their use is associated with several side effects. These are drawbacks brought about by long term use or application of potent and harmful ingredients. To ensure efficacy, skin lightening creams should be used on a prescription basis.
On the other hand, you can safely lighten your birthmarks using natural skin lightening creams. Such have no toxic ingredients and are formulated entirely from plant extracts.
How to Get Rid of Birthmarks At Home?
You can also go with natural and home remedies to either fade or improve the appearance of marks. They work by exfoliating, enhancing skin renewal and inhibiting melanin production in the pigmented area.
These remedies make use of plant extracts and at-home exfoliants. Such include papaya honey masks, yoghurt and dried orange scrubs, and essential oil massages. Natural remedies are, however, slow-acting and require to be used for an extended time for desirable effects.
Can Makeup Help with Birthmarks?
As explained earlier, some birthmarks fade with time; hence, they need not be removed immediately. The waiting can, however, take ages, especially for people who might be self-conscious as a result of the blemishes. Also, you might feel the need to conceal a birthmark due to clothing style or occasion.
To help in this, you can use makeup. The key to successful makeup use lies in adopting a regimen that works for your skin. From the primer to the blush, the routine should complement your looks and not change your appearance. With blemishes, pay attention to the foundation which should be of the same colour as your skin.
The Takeaway
Birthmarks are a common occurrence in many people. While most of them fade in childhood, others stick around for much longer. They are usually harmless though they can sometimes indicate underlying medical conditions.
The fact that a birthmark is harmless shouldn’t stop you from getting rid of it if you feel that it affects how you look or how you feel about yourself. Thankfully, you have several options at your disposal that include surgery, medication, laser therapy and topical birthmark lightening creams.